Are you
Diabetes Aware?
Awareness of diabetes is key to early detection, prevention, and better management.

Latest Ongoing on Diabetes
Types of Diabetes
The most common types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
A less common type of diabetes, called monogenic diabetes, is caused by a change in a single gene. Diabetes can also come from having surgery to remove the pancreas, or from damage to the pancreas due to conditions such as cystic fibrosis NIH external link or pancreatitis.
How common are diabetes and prediabetes?
More than 133 million Americans have diabetes or prediabetes.1 As of 2019, 37.3 million people—or 11.3%
of the U.S. population—had diabetes.1 More than 1 in 4 people over the age of 65 had diabetes. Nearly 1 in 4
adults with diabetes didn’t know they had the disease.2
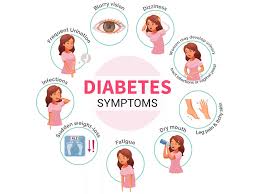
Symptoms
of Diabetes

Increased Thirst
The illness usually starts with fever, aches and pains and feeling out of sorts.

Hunger
The illness usually starts with fever, aches and pains and feeling out of sorts.

Increased Urination
The illness usually starts with fever, aches and pains and feeling out of sorts.

Blurred Vision
The illness usually starts with fever, aches and pains and feeling out of sorts.

Unexpected Weight Loss
The illness usually starts with fever, aches and pains and feeling out of sorts.

Soreness
The illness usually starts with fever, aches and pains and feeling out of sorts.
What are the Diabetes ABCs?
The A1C test shows your average blood glucose level over the last 3 months. This test is done at a health care professional’s office or lab. For most people with diabetes, their goal is an A1C level below 7%.1
Managing blood pressure is crucial for people with diabetes as high blood pressure increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. A typical target blood pressure is below 140/90 mm Hg, though lower targets may be recommended for some individuals.
Cholesterol management is essential because high levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol can lead to clogged arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The goal is to keep LDL cholesterol low, HDL (good) cholesterol high, and triglycerides in check through diet, exercise, and possibly medication.
Smoking is a significant risk factor that can worsen the complications of diabetes. It contributes to higher blood sugar levels, increases insulin resistance, and exacerbates the risk of cardiovascular diseases, which are already elevated in people with diabetes.

We want to hear from you
After visiting this site, has your knowledge and understanding of diabetes as a disease increased?


Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Research such as the Diabetes Prevention Program External link shows that you can do a lot to reduce your chances of developing type 2 diabetes. Here are some things you can change to lower your risk:
- Fitness
- Weight Management
- Diabetes and Your Health
- Medication
- Better Choices for Life Program
What are the risk factors for
type 2 diabetes?
Whether you're newly diagnosed, have been living with type 1 for years, or are helping out a loved one, the path to understanding diabetes starts here.
- Are overweight
- Are age 35 or older
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Are African American, American Indian, Asian American
- Are not physically active
- Have Prediabetes
What are the different
ways to take insulin?
The way you take insulin may depend on your lifestyle, insurance plan, and preferences. Talk with your doctor about the options and which one is best for you.
- Needle and syringe
- Pen
- Inhaler
- Syringe
- Jet injector
- Artificial pancreas
Most people with diabetes take insulin using a needle and syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. Inhalers and insulin jet injectors are less common ways to take insulin. Artificial pancreas systems are now approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Talk with your doctor to see if an artificial pancreas is an option for you.

Frequently asked Questions
Below are some answers to the most commonly asked questions about diabetes
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and unexplained weight loss. People with diabetes may also experience fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores. These symptoms arise due to high blood sugar levels affecting various body systems.
Diabetes cannot be cured, but it can be managed effectively. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy, while type 2 diabetes can often be controlled with lifestyle changes and medications. Ongoing research aims to improve treatments and eventually find a cure.
A recommended diet for people with diabetes includes focusing on:
- Whole grains: Choose complex carbohydrates like whole wheat, brown rice, and oats.
- Lean proteins: Opt for skinless poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes.
- Healthy fats: Incorporate sources such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Non-starchy vegetables: Include a variety of vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and peppers.
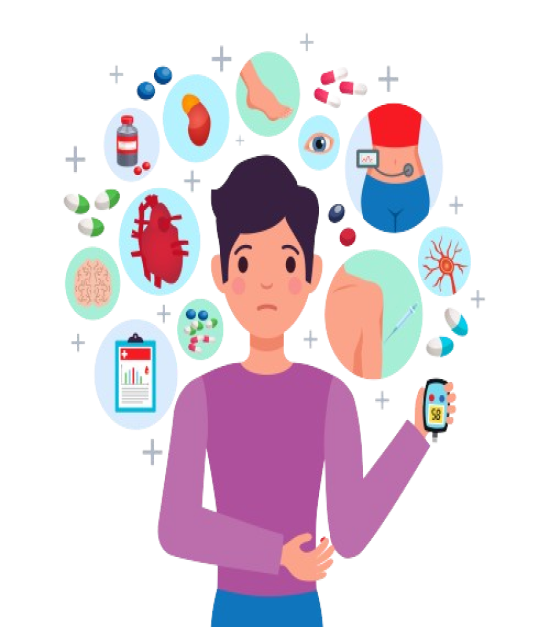
Diabetes can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), vision problems (retinopathy), and kidney damage (nephropathy). Effective management of blood sugar levels is essential to reduce the risk of these complications. Regular
Diabetes complications can be prevented by maintaining good blood sugar control through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and prescribed medications. Monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, and managing stress are also important. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers help detect and address potential issues early.
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on individual needs and treatment plans. Generally:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Blood sugar levels may need to be checked multiple times a day, including before and after meals, and at bedtime.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Monitoring frequency can vary, with some people needing to check their levels a few times a week or daily, depending on their treatment and blood sugar control.
Yes, people with diabetes can live a normal and healthy life with proper management. By following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, taking medications as prescribed, and monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can maintain good health and prevent complications. Regular medical check-ups and lifestyle adjustments also contribute to a high quality of life.